In the fall of 2019 I received an invitation to address the
board of directors for a well-known national religious organization. Knowing
that the group was largely made up of non-scientists, I accepted the invitation
and presented a talk titled “Questions asked of a molecular biologist.” The talk was followed by a time for questions
and discussion. The presentation was not recorded, but I provide a synopsis
here.
It is a special pleasure to be able to speak to you today. I
am aware of the impressive speakers that have addressed this group,
and it is an honor to be counted among them.
My goal as a professor of molecular biology and as a
Christian believer, is not to make you comfortable, but to make you think.
Thank you for the work that you do. I pray that my words
today will be clear and will magnify our view of God. Indeed, I am convinced
that our view of God always needs magnification.
I’ve chosen this topic for my remarks today – Questions
asked of a molecular biologist. I chose this topic because of what I found to
be an unexpected and remarkable experience this past year. It was the
opportunity to speak openly and honestly with a group of biomedical science graduate
students who are spiritual seekers from many different backgrounds. Two of the
students originally approached me as a faculty member and dean, knowing of my
Christian faith even as I lead an NIH-funded molecular biology research lab and
am married with two adult children. One of the seeking students had faced a
difficult year, confronted by the deaths of loved ones. She and her colleague met
me on the sidewalk one afternoon.
“Would you ever be willing to sit down and talk about
whether there is more to life beyond the experiments we do and the data we
collect?”
My answer was simple.
“Yes” I said.
“The only rule of discussion would be that I participate as
another voice in the circle – not as teacher or professor or dean. I’ll present
my path as a seeker, and explain my Christian faith, but then listen as you
speak and share and ask questions. Maybe we can discover some common questions
that lead you to wonder about whether there is more.”
The two students immediately agreed, and quickly identified
three more students to participate. These were extremely intelligent students
from across the globe, all at my institution for PhD training in biomedical
sciences. These were students from very different backgrounds. Most had been
raised in faith traditions but had become seekers because of doubt or the
disconnection between the teachings of their faiths and the realities and
questions of their professional and personal lives. The students represented
Hindu, Muslim, Roman Catholic, Evangelical Christian, and agnostic backgrounds.
All agreed to meet monthly for an hour over almost a year. The discussion
topics emerged spontaneously after each meeting and different students led
different discussions. Often the leader of the month would post one or more
readings to spur reflection or discussion before each session.
I found that many of the topics reflected ideas and
questions related to material I had already posted at
my blog,
so I commonly cross-referenced one of my essays as I provided resources for
reflection. If these kinds of topics intrigue you, I refer you to my blog as
well. In my blog I treat thoughts at the intersection of science, family, and
faith. For example, if you are curious why this professional baseball player is
holding a praying mantis on a baseball, and what that has to do with the
relationship between science and faith, you can find my discussion of the topic
here.
Although our seeking exploration covered more than a dozen
topics, I have chosen to share today four of the questions that struck me as
particularly interesting. These are topics where young scientists are
rightfully curious, and problems that skeptical trainees must confront to make
sense of a world where their personal lives and experiences are balanced with professional lives involving measurements and the reproducibility
of experiments, and ideas touching on the invisibly small molecular machines of
life.
As background, this is my church home, Autumn Ridge Church
in Rochester, Minnesota. I have been privileged to have volunteer leadership
opportunities in this large and diverse Christian congregation. I continue to
enjoy serving as a musician and I produce an Arts Series that for 13 seasons
has brought two concerts with world-class performers to Southeast Minnesota
each year.
I was raised in a church-going family that was part of a mainline denomination, but
even after baptism and first communion and confirmation, I had never come to
terms personally with the central claims of Christianity – that I constantly
fail to live up to ethical standards of my own, let alone those of a holy
and loving God, and that this God has paid a dear price to rescue me forever
from my hopeless struggle, not because I am good, but because he is good. When
I was 17 I finally understood personally the central proposition of Christianity
and made my decision to dedicate my life to God in thanks for the sacrifice of
Jesus Christ on the cross for me. This faith decision has changed everything
about how I understand the world and my place in it.
I am also a PhD molecular biologist. My BS and PhD degrees
are from the University of Wisconsin – Madison, and I did postdoctoral work at
the California Institute of Technology before beginning my career as a
professor of biochemistry and molecular biology. I have had my current research
and teaching position for 25 years.
This photo shows what I particularly love about my job – the
chance to work with brilliant young scientists from all over the world. Perhaps
it is not appreciated, but the majority of cutting-edge molecular biology that
is done to address the unknowns of how life works is done by young apprentice
scientists in their 20s. When I began my career, I was just a few years older
than my student apprentices. Now they are slightly younger than my own adult
children.
Working with extremely intelligent, skeptical, and productive
students is a prescription for staying young. Their lives are turbulent and
exciting – first partners, first jobs, first pets, first major failures and
self-doubts, first major successes, first divorces, the first illnesses and
deaths of family members, first true loneliness, first long distances from
home, first doubts about career goals.
It is exciting to be a mentor to such students.
And they find themselves asking ‘why’ questions that are
beyond the reach of the experimental science they do all day and many nights. ‘Why’
questions are every bit as important as ‘how’ questions, but science is not
designed or equipped to answer ‘why’ questions. It is the ‘why’ questions that
bring tearful students to my office to share their vulnerabilities and doubts
and fears and shame with me, not infrequently. At these ‘why’ question times I
have come to find it a privilege to listen and counsel and advise, even as the
tears can be disarming. I ask myself ‘how would I want a professional colleague
to treat one of my adult daughters at a stressful time such as this?’
It was in this context that I agreed to participate in a
discussion of hard questions asked by very smart, seeking students. In many
ways the student-requested discussion was something I had always hoped to do,
and perhaps something I will do again.
I think what made me especially comfortable with it was that
I wasn’t my idea.
So here are four of our group questions that I’ve chosen to
share today.
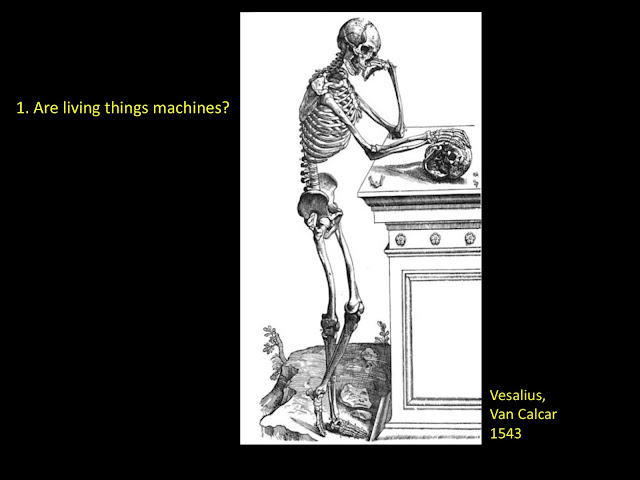
Let’s begin with the first. “Are living things machines?”
In a sense, the answer is simple, and we know that it is
“yes,” especially because of the work of Vesalius and van Calcar, as shown in
this beautiful rendering from 1543. All living things are flesh and bone, bark
and root at the macroscopic level, built from levers and pumps, sinews, meat
and blood, tissue. Recognition of our own mechanistic character by dissection was
one of the pillars of the enlightenment. Vesalius, da Vinci, Harvey all made
seminal contributions.
But I’m here to answer the question with a more fundamental
‘yes’ than Vesalius or da Vinci or Harvey could have given. I’m here to affirm
that living things, all of us, are digital machines all the way down to the
nano level.
In fact, this is the realm of nanomachinery where I work. These
nanomachines are millionths of inches small, invisible, but
still absolutely mechanistic. The DNA code molecule shown in this picture is a
mechanical ladder where the segment of rungs shown here is a millionth of an
inch long, but the three billion rungs of ladder code in each human cell add up
to 6 feet of invisibly thin double helix, packed with digital instructions
encoded as a linear hard drive – two copies of every inherited instruction, one from mom, one from
dad, needed to make another entire human identical to us.
Indeed, we are machinery all the way down to the nanodevices
that form our cells.
The idea that DNA carries all the coded recipes for all of
the nanomachines of life has always delighted and fascinated me. That’s why I
still have this 6-foot-tall poster on the wall outside my office at work. It
shows the map of the coded blueprint information, the recipe locations, for the
20,000+ recipes for all the nanomachines needed to make a human cell. The
recipes have all been sequenced now – we know the code, so we can read this book
of life and labs like mine study how the code is organized, how only some
recipes are used at any given time, and what goes wrong when recipes have
errors or are read at the wrong time and place in cells.
If we zoom in on this map, we start to see the locations of
individual recipes, written into stretches of thousands of rungs of DNA ladder
code, all coiled and folded and packed into volumes like a huge, complicated
cookbook of recipes, organized in unexpected and perplexing ways.
We, and all living things, are machines all the way down to
the nano scale. Here is an example of our digital code, written with the
letters G,A,T,C to substitute for the chemical rung structures of DNA.
The code
is read out by a copying machine and then a translation machine so the string
of DNA is first rendered as an RNA copy, but then interpreted by translation so
each group of three original DNA letters corresponds to one ‘bead’ on an
eventual string of amino acid beads, that will fold into the functional protein
nanomachines of life. These invisibly small proteins become the meat and bone
and goo of living things.
How cool that scientists before us figured out this genetic
code! How absolutely cool that all living things share the same code – there is
just one universal digital language shared by everything that is alive – and we
can read it! We scientists can copy and paste digital recipes and rewire cells
to do new and different things – all because we are machines all the way down
to the nano scale, and machines built from coded instructions, and coded
instructions of just a single language for all living things.
In this example, the recipe code starts at
the letters “ATG” and ends at the letters “TAA” with each triplet between indicating
a different one of the 20 possible amino acid ‘beads’ forming this string that
folds automatically to form this machine that we study in our lab.
This particular machine shown in red is part of a larger
machine. We study it because when it is broken or missing, cells can grow out
of control and become cancerous tumors.
Now here is something incredibly cool. Because we can read
the genetic recipes written in the DNA of different living things, we can
compare these recipes! In fact, it soon became clear that all living things are
built from similar recipes, and the same kinds of nanomachines are doing their
things in all of us, from humans to other animals, plants, bacteria…everything.
Here I have lined up the genetic recipes for one of the
machines my lab studies in humans. The recipes for this machine are shown for
bacteria, yeast, humans, and pigs. The recipes are shown with 20 different
letters to represent the 20 different amino acids coded by the sequential
triplets of G,A,T,C DNA letters I showed earlier. If we look at the code
sequences for this nanomachine we quickly realized that the codes look similar!
We can recognize the patterns and in some places the codes for this machine are
identical in bacteria and humans! Where the codes aren’t identical, they are
often similar. This machine is quite similar, even interchangeable, across many
living things.
Not only are living things machines, but the digital codes
in living things can be compared.
This was a HUGE discovery, because it means that we don’t
have to just compare how living things look on the outside, we can actually
read the instruction blueprint for each kind of living thing and compare the
blueprints.
Scientists quickly came to terms with the similarities
between living things:
This is where I want to share a very important point.
Without any ax to grind, scientists began comparing the digital codes in living
things. Scientists did something kind of obvious – they used the kinds of
comparison tools used to compare the familiar codes that we humans call
languages.
Few people doubt that languages are related, and that
languages have descended from common ancestors. We see this in the similarities
of certain languages, and we can recognize the sounds of words in other
languages descended from common ancestors.
In fact, languages evolve. They change over time. As
groups of people become separated, their languages drift and become different
enough that different language groups can no longer communicate.
Here is a common tree diagram depicting the relationship
between languages. The common ancestor languages can be deduced. I’ve never heard
anyone claim that all languages were created at once in their present forms. It
is self-evident from the codes that languages descended from common ancestors
over long times.
Charles Darwin studied the macroscopic external appearance
of plants and animals and deduced common ancestry, proposing an evolutionary
theory for the relationship between all living things. Darwin did this based
only on what he saw, kind of like trying to propose relationships between
languages based only on how they sound.
How amazing was it then when, more than a century later,
scientists realized they could compare the DNA codes inside of living things.
This is like comparing languages as written codes rather than just by listening
to the sounds of the words.
What became instantly clear is shown here. The same tools
that show relationships between languages through common ancestors forming a
language ‘tree’ revealed an absolutely analogous ‘tree of life.’ The best and
most obvious explanation for this tree is exactly the same explanation as for the
language tree – living things have evolved over time from common ancestors.
This wasn’t an evil scheme to destroy religious faith – it
was simply the realization that Darwin’s insight based on appearances had been
shown to be correct by reading the digital codes built into every living thing.
Amazing.
So are living things machines? Yes. From what we can see right down to the
nanoscale, they are all machinery – we are all machinery. And the digital
coding of life makes it absolutely obvious that all living things are related
to each other – and since the relationship looks just like the relationship
between languages that have evolved from each other over long periods of time
with change and separation, evolution over a long period of time is the obvious
logical conclusion of this discovery that living things are machines based on
digital code.
This "yes" conclusion prompted an obvious question in our
discussion group. If living things are material, and the enlightenment moved us
away from animism to a mechanistic view of life, is there any room left for the
concept of a soul – an aspect of life that is beyond the mechanical – an aspect
that might commune with a higher power, a creator if there is one – an aspect
of life that lies on the ‘why’ dimension – an aspect of life that might
transcend the mechanical and outlive the machinery?
What is a soul?
What a great question. I have blogged about this question
in the past, so we discussed a possible direction for thinking about the soul. My argument
has been based on the concept of
emergent
properties – properties of large and complex systems that are not readily
explained by the properties of the component parts.
My analogy relates to the concept of ant colony behavior
that isn’t predictable by studying individual ants. Ants are cool, but…
Ant colonies do lots of things that individual ants do not.
These colonial behaviors are kinds of emergent properties observed only when
hundreds or thousands of ants work together and we start to realize that there
is a kind of ant colony “organism” that we only understand when we grasp that we can't understand the purpose of an
individual ant, its ‘why,’ until we see it in context.
There is a possible analogy that gets us to the soul. It is
the analogy between ant/colony and neuron/brain. It is entirely plausible that
the 100 billion neuron cells of the human brain are the ants and the brain is the
colony, replete with emergent properties unpredicted by the characteristics of
neurons. These are properties like self-awareness, consciousness, selflessness,
love, and the longing for connection to a purpose and the sensed yearning for
the love of a creator.
I think this is such an interesting idea.
And it has fascinating implications that our group
discussed.
First, if the soul is an emergent property of a complex
brain, we must confront the fact that humans are not the only animals with
complex brains. Are all creatures machines, but only humans have brains
large enough to spawn emergent souls that are loved by a creator God and can
commune with that God beyond this life? What if the different brains of all
kinds of creatures generate different kinds of souls that are loved and find
transcendence with such a God?
Wow.
Second, if the soul is an emergent property of a complex
brain, what happens when that brain dies? An ant colony has no emergent
properties when all individual ants are dead. There is no immortal emergent
property of an ant colony except perhaps our memory that such a colony once
existed. What of a soul that is an emergent property of a living brain? When
the neurons cease to function, what of that soul? Here we discussed the notion
of reincarnation, or in Christian terms, resurrection. If the soul is an
emergent property of a complex brain, the soul is immortal if that physical brain
can somehow be made immortal by resurrection – re-integration – recreation. If that brain is physically rebuilt in a manner that is timeless, a
timeless soul re-emerges.
So, though by no means a trivial idea, the fact that living
things are machines does not kill the idea that a transcendent soul could
emerge from a complex mechanical brain. Such a soul is a way to understand the
aspects of human life whose aesthetics provide ‘why’ answers in a mechanical
universe that otherwise lacks them. As I have discussed in a
previous post the idea that answers to ‘why’ questions are totally fair and desirable even
though such answers are off limits for experimental science.
Our discussion group was made up of students trained in
molecular biology, though each was studying different fields and questions. The
group did find itself discussing the ethics of application of technology to the
mechanism of living things. Since living things are machines, and since we
increasingly understand that machinery, we are learning to engineer it. In some
ways this is the story of medicine, and in some ways it is also the ancient
story of selective breeding. The latter is just genetic engineering done in
slow motion and without mechanistic insight.
But what of newer and faster techniques that allow us to
engineer the digital blueprints present in the DNA of all living cells? As we
change this blueprint information, we change the character of the cell. As that
cell divides, we have the potential to change the character of the resulting
organism – or even to make new kinds of organisms. Is this something to worry
about?
The reason this is on our minds is the discovery and optimization
of a wonderful and unexpected technology found buried within the deep inner
workings of bacteria. This is an ideal example of a principle that I try to
communicate to the lay public every chance I can – the revolutionary
discoveries that change medicine for humans almost exclusively come from
studies driven by curious scientists simply interested in how living things
work, very often without any obvious connection to human health. This is one of
the reasons why it is so important to promote and support the work of curious
scientists – we simply don’t know what is going to turn out to be important for
human medicine.
This is also exactly the case for the discovery of the
CRISPR/Cas9 machinery hidden in bacteria.
We simply had no idea that bacteria carry their own immune
systems, helping them fight off their own parasites!
Who knew?? We think of bacteria being the parasites, but they themselves have been in an ancient
battle with their own parasitic viruses (called bacteriophages) and dangerous
parasitic mobile DNA molecules.
The name of the CRISPR system (an acronym standing for clustered regularly interspaced short
palindromic repeats) illustrates the accidental way in which the system was
discovered. The molecular nanomachinery that performs the immune functions was
not discovered first. Rather, it was peculiar features of the genetic blueprint
instructions for CRISPR in the bacterial DNA that caught the attention of DNA
sequencing bacteriologists before they had the slightest ideas what was encoded
by these DNA patterns. Remarkably, bacteria with CRISPR systems preserve a
digital record of samples of the DNA codes of invading parasites so this
library of code specimens is ready in the DNA blueprint of the bacterium
itself, allowing every piece of DNA to be checked against this library, for
safety.
Amazing? It is like
a facial recognition system to destroy anyone depicted on a ’10 most wanted’
poster.
To appreciate this natural and unexpected bacterial
technology and how it has been re-engineered by clever scientists, consider
another analogy that I used in our group’s discussion of the ethics of
CRISPR/Cas9. This analogy is a simple zipper.
The double-stranded DNA in cells is a molecular ladder
twisted into a spiral, and it is in some ways like a zipper. The analogy is not
perfect, but it is surprisingly good. We just have to remember that unlike the
identical teeth in the zippers in our clothes, DNA zipper teeth come in 4
shapes, and the DNA zipper can’t zip unless the teeth match in a complementary way – DNA
is a smart zipper.
Amazingly, the CRISPR system is like the single red zipper
strand shown here without a partner. Let’s imagine that in this room full of
people wearing clothes with zippers, each person’s zipper is slightly different
as far as the sequence of the zipper teeth. If one of us is a dangerous
criminal, how might we be detected? How about a zipper ID test? Let’s say we
have a record of the order of teeth on one section of the criminal’s zipper,
and it is available as this single red probe zipper. One way to find the
criminal is to allow this single red probe zipper to test for matches with all
the zippers on the clothes of the people in this room.
Seems crazy, but that is exactly how the CRISPR system
works.
The CRISPR system has a zipper tab that can start probing almost
anywhere along any zipper. Prying into the target zipper, it inserts its red
single zipper and tests for a match to the potential criminal sequence by
zipping.
Most zipper teeth won’t match and the CRISPR system then disengages
harmlessly. However, if a perfect match is found all the way along the
teeth of the red single probe zipper, the fully-zipped product triggers a
clever machine that physically cuts the target zipper so it can no longer close.
[Reflect for a moment on the implication in the analogy for
the criminal in this room if the recognized and destroyed zipper is the one
that keeps the criminal’s pants closed.]
Here is a molecular view of the actual CRISPR/Cas9 machinery,
also less than a millionth of an inch in size. I colored it so the red single
zipper is red, and the grey target zipper whose tooth order is being checked is
grey. In this picture, the green stuff is the protein that acts as both the
zipper tab that is inserted in the target zipper to do the checking, and the
scissors that are activated if a perfect match is found.
Our discussion group, being made up of molecular biologists,
was somewhat familiar with this molecular machine, so we reviewed it as well as
its unlikely discovery within bacteria, and its subsequent engineering. This
engineering means that the little machines can now be engineered with whatever
red single zipper tooth sequence we want, so the machines will scan and cut
target DNA zippers only where we wish.
Cutting a target zipper DNA in a living cell has the
interesting effect of triggering the cell to undertake a haphazard repair
attempt that results in a repaired zipper with a kind of scar that has a slightly different sequence of
teeth than the original, often destroying the meaning of the code. These errors
can destroy the genetic recipe encoded by the target zipper sequence, allowing
scientists to edit (crudely for now) the recipe list.
One of the big challenges is getting the red single zipper
inside of cells where it can do its job. That’s one of the things we work on in
our lab, but that is also a different story…
So, the question our group asked was whether we should be
alarmed by the availability of this CRISPR technology, stolen from bacteria,
and engineered to alter gene recipes in any organism, including humans.
The group reflected on the fact that this kind of gene
editing might be applied in two general ways.
If the gene edit is made in a normal body cell (a “somatic”
cell) of an organism such as a human patient, the change stays in that patient
and is not passed along to offspring.
If, however, doctors or scientists figure out how to make
the gene change in one of the eggs or sperm ( the ‘germ cells’) of a human
patient, their DNA is then included in the new fertilized embryo to create the
genetic recipes for the baby. In fact, every single one of the trillions of
cells in the resulting baby would inherit the same gene change made by CRISPR
in the egg or sperm. Such technology has powerful implications that have
already triggered ill-considered attempts to alter eggs so the resulting babies
have a designed gene change in every cell. These changes would then be
inherited by their offspring, and the human race altered a little bit by the
effort.
Such “germline” gene editing is currently illegal, and our
group agreed that it is premature to consider the idea of “medicine” that
alters families now and in perpetuity. We’re just not smart enough to
understand the implications of this kind of medicine.
On the other hand, editing DNA within the somatic cells of
an individual patient is not nearly as ominous, as the effects are limited to
that individual.
We concluded that we should not be alarmed by the
availability of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology. It is a tool, neither good
nor bad. We should explain the tool to the public, and help guide ethical use
of the tool. For now, that means limiting its use to the editing of somatic
cells where it may be of use as a new kind of precision medicine in some
patients.
This then brings us to a fourth discussion topic that I
found particularly interesting.
The students asked why so many Christians are so
frightened by the ideas of an ancient earth and evolutionary origins. As
scientists, we wanted to appreciate the source of these fears and concerns in
order to improve our dialog with Christian people who feel threatened by these
very important scientific concepts. We also wanted to explore whether there is
something about Christianity that is inconsistent with the findings of science.
Are Christianity and science complementary ways of
discovering and understanding the same truth, or are they inconsistent?
Those familiar with my blog know that I’ve posted several
things about this issue before –
here,
here,
here, and
this video.
As we discussed with our discussion group, I believe the
central issue comes down to this illustration and how we choose to understand
the written documents of Judaism and Christianity, what we call the Old and New
Testaments of the Bible. Christians derive their understanding of God from
these documents, and Evangelical Christians believe that the documents are
worth studying. The question is ‘in what sense are these documents true?’ Some
Christians see the biblical documents as if they were a textbook, all written
in one coherent format, as if by one author, all for one purpose. I show here one
of my favorite textbooks, Richard Feynman’s Lectures
on Physics, as an example. Textbooks are one kind of literature, and we
understand them by studying them in a certain way.
I have argued that the Bible is not a textbook. It
is much more interesting than that. The Bible is a scrapbook.
Scrapbooks (at least those like my own scrapbook, shown here) are full of
mysteries and surprises and puzzles, contradictions, delights.
The Bible is a scrapbook and it does not reveal many ‘how’s (as it would if it were a textbook), but it does reveal many ‘why’s. This makes
it a particularly unique and important collection of documents reflecting the
contributions of dozens of authors over centuries of time.
So, part of the fear of some Christians about scientific
evidence for an ancient earth and evolutionary origins can be traced to the
desire to read and understand the Bible as a textbook.
We discussed another likely contributor to discomfort about
an ancient earth and evolutionary origins – the truth of these concepts tends
to reduce the special importance of humans.
This is a problem because we like to be especially
important.
I like this quote from pastor Rick Warren. Rick makes the
point that we like to think of the universe from the reference frame of…us. The
Bible meets us in this reference frame, but that doesn’t mean that it is the
ultimate reference frame – it is simply the only reference frame our tiny minds
can comprehend.
It hasn’t taken long for modern instruments descended from
Galileo’s original telescope to remind us that our place in the universe is
insignificant, as is the amount of time we have been living here.
Sobering but true.
Our discussion group thus decided that another reason some
chafe against an ancient earth and evolutionary origins is that we find
ourselves no longer the main event, the stars of the show. We are told in the
Bible that we humans are specially loved and that have been purchased by God
through an expensive and mysterious sacrifice.
But this doesn’t mean that we are unique. It doesn’t mean
that God has no other love stories in other places, times, or universes.
This image of earth from beyond Saturn might please Galileo,
who was the first to see moons circling Jupiter, reminding us that the earth is
not the center of everything.
In fact, the earth is the center of very little.
As I have
posted,
our place in the universe is unimaginably small. That a powerful and creative
God is at all mindful of us is the miracle. The size of our planet relative to
the size of known universe is on the same order as the size of a grain of sand
relative to the size of the entire planet earth. On that massive scale the
single sand grain is too small to matter – isn’t it?
Our group discussed my post that we humans may dislike the
idea of evolutionary origins because it destroys the sense that human history
is a significant part of the history of the universe.
It isn’t. The 10,000 years of recorded human civilization
are to the age of the universe as the last two seconds of time are to the
previous month. Inconsequential. Insignificant.
In the world we are discovering through science, the space
and time of humanity lose their prime status. Rather than being obvious that a
loving God must attend to us, it becomes unfathomably remarkable that we merit
the least notice in the blink of time that we have occupied this dark corner of
what may be just one universe of a multiverse.
No wonder some are discomforted by the ideas of an ancient
earth and evolutionary origins. These ideas force us to rethink the Bible as
textbook, requiring more homework to unpack the purpose of the biblical scrapbook.
These ideas also force us to confront our insignificance.
Apparently the only reason our human story is important is because
God says it is.
Our group discussed how these are not particularly new
ideas, but they have been rediscovered over and over in history. This is one of
the great reasons to study history and literature – to realize that we may be re-fighting
intellectual battles that were already won by thinkers like Augustine and Galileo
centuries ago. In his The Language of God,
molecular biologist Francis Collins calls these the Lessons of Galileo.
I smile audaciously to then contribute my own quotation along the same
line, and it sums up what our discussion group concluded in considering an
ancient earth and evolutionary origins.
So, we come to the conclusion of this story of a remarkable
group of seeking students and their willingness to ask important questions of a
molecular biologist.
They knew that I have lived my live as a professional
scientist and as a person of faith. They wanted some insight into how that combination
can coexist. By the end of our sessions together, I had shared my own path to
Christian faith, and I had tried to be honest and vulnerable about the feelings
of guilt and loneliness that led me to investigate, and eventually accept, the
claims of Jesus Christ.
We then talked about more than a dozen topics, including the
four summarized here.
Thank you so much for your attention. Let’s have some
discussion!
1.14.20
A reader comments:
I enjoyed reading your presentation - rigorous discussion around very complex topics. I am not a young earth proponent, but I do have one question: What is the difference between the DNA building blocks evolving over millions of years, like languages, into different species versus God using those building blocks to design life in more real time? Does the DNA profile look the same either way? Is the only difference the amount of time God used to complete the task (allowing / guiding macro evolution vs. a more "fast path" or micro evolution approach)?
Response:
Great question.
I use the language analogy to get us thinking. The biblical story of Babel (Genesis 11:1-9) might suggest that God created all the different languages at once by confusing the speakers of one original language with a single act. That’s what we would deduce if the Bible is a textbook. If the Bible is a scrapbook that includes stories and mythology meant to help explain things that are hard to explain (like different languages), then we are open to the possibility that the real origin of languages is different from the Babel story, or perhaps better stated, that the Babel story doesn’t likely explain the different languages we experience today. By studying the languages of today, we see that they are related in a way that points to common ancestry, and we can make diagrams that illustrate the likely family tree. As we watch language evolution we see that it is slow. It therefore seems more reasonable to explain the family tree of languages as being the result of a slow process of evolution, based on the principle that it is simplest to assume that processes currently observed are generally similar to processes that took place in the past. That means language evolution has been taking place over many thousands of years. Could God have created all languages in their current form very quickly, and then just created the appearance of a family tree of relationships because that is beautiful? Sure. God can do almost anything except be untrue to himself. It is just easier to understand languages as having arisen by gradual processes. The only reason not to believe that is if we insist that the Babel story is taken as a textbook account and applied universally to all languages.
So, the same goes for the genetic relationships between organisms. Could God have quickly created all the kinds of organisms using a process that created the appearance of the genetic family tree that we see by gene sequencing, including genetic parasites and broken genes? Of course he could have. He can do almost anything. However, based on what we see going on now, and processes and the measured pace of genetic changes, and based on the assumption that current processes are generally a reasonable model for past processes (the simplest assumption of science where miracles aren’t invoked), the time to build the current genetic tree of life would be thousands of millions of years. This doesn’t mean that remarkable things like asteroid impacts haven’t occurred in earth history, so unusual events are allowed. My argument is that the simplest explanation for the tree of life, as for the tree of languages, is a long, slow process that appears random even if it is, in fact guided by God. Simplest explanations win in science. The only reason to invoke the hand of God in a sudden process that just imitates the slow process is insistence on understanding the Bible as if it were a textbook.
I’m quite convinced that the writers of the Bible never claim that it is a textbook (!), or that it should be understood as a homogeneous and uniform document containing a single style of literature. That’s why it doesn’t bother me at all to choose the simpler explanation that is more consistent with what we observe with our eyes and experiments, rather than reverting to seeing the world through the lens of a textbook reading of the Bible.
After all, it was insistence on a textbook reading of the Bible that suggested a geocentric universe, and that got Galileo in trouble when he found moons orbiting Jupiter rather than earth. My argument is that we long-ago learned that the textbook view of the Bible is not particularly valuable in astronomy and cosmology. We all pretty much understand that now.
It is taking longer to realize that the same is true for languages…and biology ☺.
The reader comments again:
That is a very helpful explanation, and I don't necessarily disagree with it. I am not convinced, however, that just because one thinks there was miraculous intervention (i.e God sped up the process from what we observe today) it means that one reads the Bible as a textbook. I don't make that connection. I think the overwhelming scrapbook story of Scripture is that God intervened. He certainly intervened in the incarnation. He could have also intervened in creation - and in fact did at some point in the process. "In the beginning God (vs. chance) created the heavens and the earth." It seems to me we can have differing views of how he created and over what period of time without thinking of Scripture as a textbook. Thoughts?
Response:
Yup. Good thoughts.
I would just make some comments about the concept of God “intervening.” Though it is debated by theologians, my personal conviction is that God exists outside of time, and created time for his purposes without needing to exist within it. This is analogous to a playwright or composer creating an artistic product in the dimensions of her own existence. While the actual performance of the piece and its characters are trapped in time and space, the creator is not. Because we are creatures of the time dimension (akin to characters in the play), we have no real ability to fathom what the existence of the playwright (outside of time) is like. We are trapped in time and can only think about timelessness by analogy. My sense that God is timeless is based on hints from the Bible, and my instinct that God is master of everything, so of time as well. I could be wrong.
The reason that prior paragraph matters is that, if it is true, it means that God has never ‘intervened’ in the sense of inserting himself into a place or plot where he wasn’t previously involved. It’s like saying that the playwright became involved in her play only here and there. That doesn’t make any sense because the playwright is responsible for the entire play from conception to crafting of plot to conclusion. The playwright might choose to write herself into the play as a character here and there, so both audience and other characters would get to know her character, and she might even create plot lines where her actions in time have dramatic and real consequences for the other characters in the play. I would not say that this would be intervention. She wrote the whole play and just chose to enter the plot as a character here or there. The whole play was written knowing of those plot twists.
So I see God as having written into the fabric of time and space and what we perceive as random chance the plot and the story, right from what we see as the start, right through to what we will see as the end. We can’t conceive it because we are creatures of time. He has accomplished this to allow for what we perceive to be free will and he knew the outcome before setting the story in motion. Indeed, that is the most encouraging thing about this universe – that God told/is telling/will tell a beautiful story well worth telling, though we see it incompletely from the perspective of time.
Now as to God being able to manipulate time for his purposes, obviously from my comments above, he can do this if it suits him. I am more concerned in my advocacy for science and Christianity with the issue of credibility. This was the point of the slide with the quote from Augustine in my talk. If we stubbornly cling to certain textbook interpretations of biblical treatments of science and cosmology and astronomy and biology and other areas that the ancient authors could not address with any authority or insight, we risk discrediting ourselves as not having a message worth hearing on matters of faith and salvation. The world is suspicious that they will need to deny the implications of objective observation if they want to accept the Gospel. They do not. I think the “foolishness” of the message of the cross for those who are perishing (Paul’s first letter to the church at Corinth, 1:18) has nothing to do with Christians needing to ignore scientific evidence staring them in the face, it has to do with the paradox of losing one’s life to gain it.
By wrapping Christianity in an anti-intellectual package, we create an unnecessary obstacle, particularly in a city like ours. I think this is one of the central discussions for Christian leaders here over the coming years.
I am about removing obstacles.